记录自定义LLM追踪
如果您没有以正确的格式记录LLM追踪,不会有任何问题——数据仍将被记录。但是,数据将不会以LLM特有的方式进行处理或渲染。
LangSmith 为 LLM 追踪提供特殊的渲染和处理,包括 token 计数(假设模型提供商没有提供 token 计数)和基于 token 的成本计算。为了充分利用此功能,您必须以特定格式记录您的 LLM 追踪。
聊天风格模型
使用 LangChain OSS 或 LangSmith 包装器
如果您正在使用 OpenAI 或 Anthropic 模型,我们建议使用 wrap_openai 或 wrap_anthropic,它们将自动以 LangSmith 期望的格式记录追踪。
您还可以使用任何 LangChain OSS 聊天模型 作为直接访问任何提供商 API 的替代方案,这也会以 LangSmith 期望的格式记录 LLM 追踪。
实现您自己的自定义聊天模型
您也可以使用 traceable 或其他更广泛的追踪技术来追踪您的模型调用。在这种情况下,要正确地将追踪函数标记为 LLM 运行,至少必须将 run_type 设置为 "llm",如下所示:
- Python
- TypeScript
from langsmith import traceable
@traceable(run_type="llm")
def chat_model(messages: list):
...
import { traceable } from "langsmith/traceable";
const chatModel = traceable(
async (messages) => {
// Call the model here
},
{ run_type: "llm" }
);
为了让您的自定义 LLM 追踪在 LangSmith UI 中良好格式化显示,您的追踪输入和输出必须符合 LangSmith 识别的格式
- 以 OpenAI 或 Anthropic 格式表示的消息列表,表示为 Python 字典或 TypeScript 对象。
- 每条消息必须包含 `role` 和 `content` 键。
- `"assistant"` 角色的消息可选地包含 `tool_calls`。这些 `tool_calls` 可以是 OpenAI 格式或 LangChain 的格式。
- 一个字典/对象,其中包含键 `"messages"`,其值为上述格式的消息列表。
- LangSmith 可能会在此输入字典中使用与 OpenAI 聊天完成端点 匹配的其他参数,以便在追踪视图中进行渲染,例如模型可以调用的可用
tools列表。
- LangSmith 可能会在此输入字典中使用与 OpenAI 聊天完成端点 匹配的其他参数,以便在追踪视图中进行渲染,例如模型可以调用的可用
这里有一些例子
- 消息列表
- 消息字典
# Format 1: List of messages
inputs = [
{"role": "system", "content": "You are a helpful assistant."},
{"role": "user", "content": "What's the weather like?"},
{
"role": "assistant",
"content": "I need to check the weather for you.",
"tool_calls": [
{
"id": "call_123",
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "get_weather",
"arguments": '{"location": "current"}'
}
}
]
}
]
@traceable(run_type="llm")
def chat_model(messages: list):
...
chat_model(inputs)
# Format 2: Object with messages key
inputs = {
"messages": [
{"role": "system", "content": "You are a helpful assistant."},
{"role": "user", "content": "What's the weather like?"}
],
"tools": [
{
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "get_weather",
"description": "Get current weather",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"location": {"type": "string"}
}
}
}
}
],
"temperature": 0.7
}
@traceable(run_type="llm")
def chat_model(messages: dict):
...
chat_model(inputs)
输出接受以下任何一种格式
- 一个字典/对象,包含键 `choices`,其值为字典/对象列表。每个字典/对象必须包含键 `message`,该键映射到一个包含 `role` 和 `content` 键的消息对象。
- 一个字典/对象,包含键 `message`,其值为一个包含 `role` 和 `content` 键的消息对象。
- 一个包含两个元素的元组/数组,其中第一个元素是角色,第二个元素是内容。
- 一个包含 `role` 和 `content` 键的字典/对象。
这里有一些例子
- 选项格式
- 消息格式
- 元组格式
- 直接格式
from langsmith import traceable
@traceable(run_type="llm")
def chat_model_choices(messages):
# Your model logic here
return {
"choices": [
{
"message": {
"role": "assistant",
"content": "Sure, what time would you like to book the table for?"
}
}
]
}
# Usage
inputs = [
{"role": "system", "content": "You are a helpful assistant."},
{"role": "user", "content": "I'd like to book a table for two."}
]
chat_model_choices(inputs)
from langsmith import traceable
@traceable(run_type="llm")
def chat_model_message(messages):
# Your model logic here
return {
"message": {
"role": "assistant",
"content": "Sure, what time would you like to book the table for?"
}
}
# Usage
inputs = [
{"role": "system", "content": "You are a helpful assistant."},
{"role": "user", "content": "I'd like to book a table for two."}
]
chat_model_message(inputs)
from langsmith import traceable
@traceable(run_type="llm")
def chat_model_tuple(messages):
# Your model logic here
return ["assistant", "Sure, what time would you like to book the table for?"]
# Usage
inputs = [
{"role": "system", "content": "You are a helpful assistant."},
{"role": "user", "content": "I'd like to book a table for two."}
]
chat_model_tuple(inputs)
from langsmith import traceable
@traceable(run_type="llm")
def chat_model_direct(messages):
# Your model logic here
return {
"role": "assistant",
"content": "Sure, what time would you like to book the table for?"
}
# Usage
inputs = [
{"role": "system", "content": "You are a helpful assistant."},
{"role": "user", "content": "I'd like to book a table for two."}
]
chat_model_direct(inputs)
您还可以提供以下 `metadata` 字段来帮助 LangSmith 识别模型——如果识别成功,LangSmith 将自动计算成本。要了解如何使用 `metadata` 字段,请参阅本指南。
ls_provider: 模型的提供商,例如 "openai"、"anthropic" 等。ls_model_name: 模型的名称,例如 "gpt-4o-mini"、"claude-3-opus-20240307" 等。
- Python
- TypeScript
from langsmith import traceable
inputs = [
{"role": "system", "content": "You are a helpful assistant."},
{"role": "user", "content": "I'd like to book a table for two."},
]
output = {
"choices": [
{
"message": {
"role": "assistant",
"content": "Sure, what time would you like to book the table for?"
}
}
]
}
# Can also use one of:
# output = {
# "message": {
# "role": "assistant",
# "content": "Sure, what time would you like to book the table for?"
# }
# }
#
# output = {
# "role": "assistant",
# "content": "Sure, what time would you like to book the table for?"
# }
#
# output = ["assistant", "Sure, what time would you like to book the table for?"]
@traceable(
run_type="llm",
metadata={"ls_provider": "my_provider", "ls_model_name": "my_model"}
)
def chat_model(messages: list):
return output
chat_model(inputs)
import { traceable } from "langsmith/traceable";
const messages = [
{ role: "system", content: "You are a helpful assistant." },
{ role: "user", content: "I'd like to book a table for two." }
];
const output = {
choices: [
{
message: {
role: "assistant",
content: "Sure, what time would you like to book the table for?"
}
}
]
};
// Can also use one of:
// const output = {
// message: {
// role: "assistant",
// content: "Sure, what time would you like to book the table for?"
// }
// };
//
// const output = {
// role: "assistant",
// content: "Sure, what time would you like to book the table for?"
// };
//
// const output = ["assistant", "Sure, what time would you like to book the table for?"];
const chatModel = traceable(
async ({ messages }: { messages: { role: string; content: string }[] }) => {
return output;
},
{ run_type: "llm", name: "chat_model", metadata: { ls_provider: "my_provider", ls_model_name: "my_model" } }
);
await chatModel({ messages });
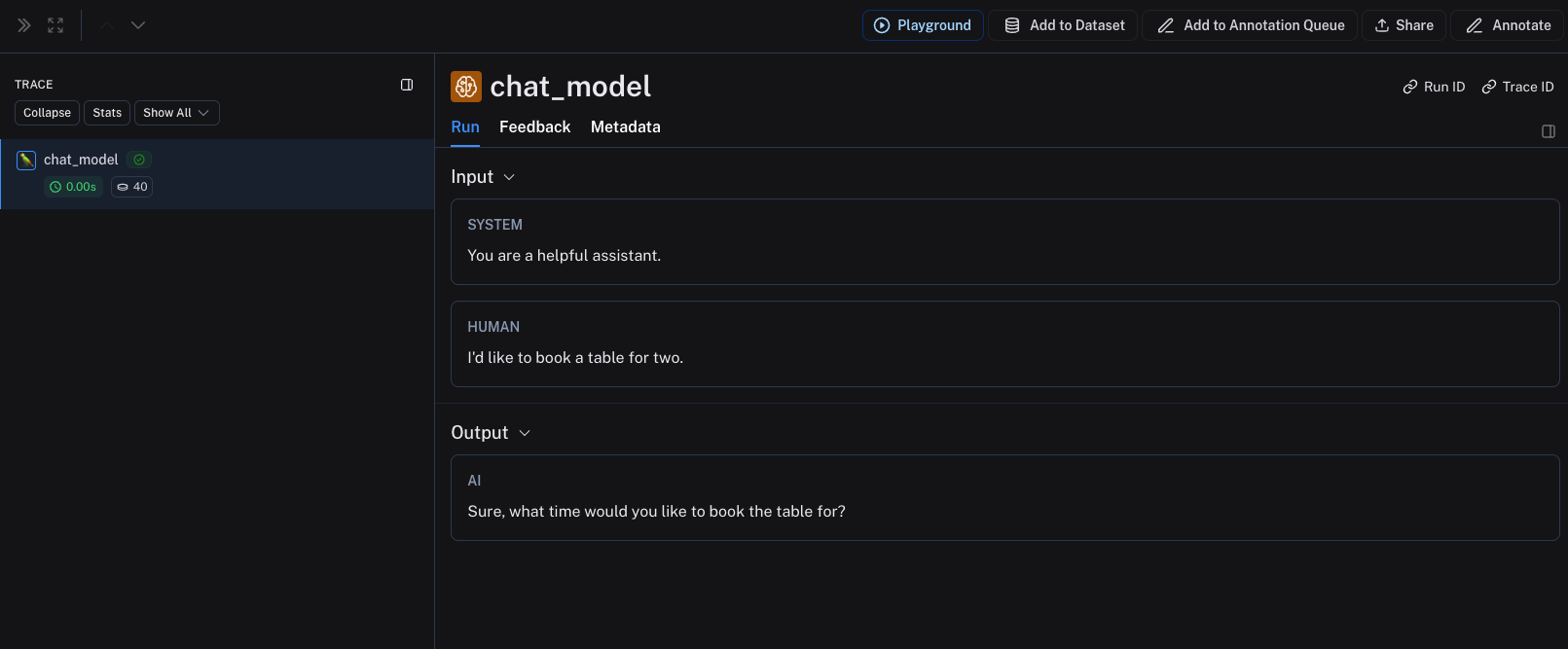
以上代码将记录以下追踪
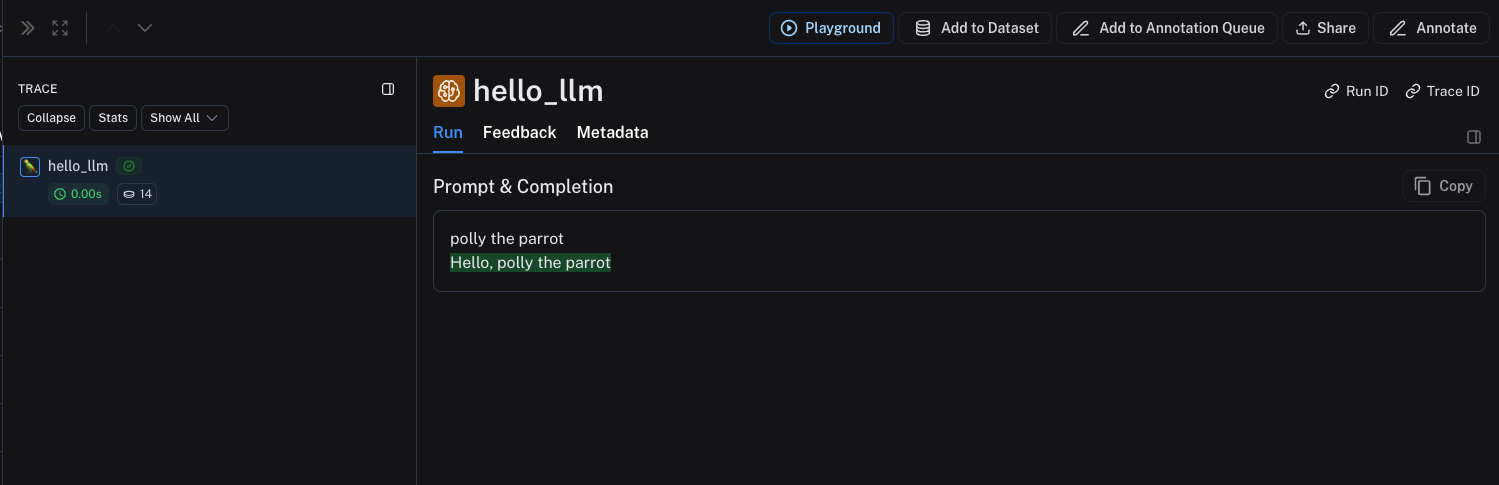
如果您实现了自定义的流式聊天模型,您可以将输出“简化”为与非流式版本相同的格式。目前这仅在 Python 中支持。
def _reduce_chunks(chunks: list):
all_text = "".join([chunk["choices"][0]["message"]["content"] for chunk in chunks])
return {"choices": [{"message": {"content": all_text, "role": "assistant"}}]}
@traceable(
run_type="llm",
reduce_fn=_reduce_chunks,
metadata={"ls_provider": "my_provider", "ls_model_name": "my_model"}
)
def my_streaming_chat_model(messages: list):
for chunk in ["Hello, " + messages[1]["content"]]:
yield {
"choices": [
{
"message": {
"content": chunk,
"role": "assistant",
}
}
]
}
list(
my_streaming_chat_model(
[
{"role": "system", "content": "You are a helpful assistant. Please greet the user."},
{"role": "user", "content": "polly the parrot"},
],
)
)
如果 `ls_model_name` 不在 `extra.metadata` 中,则 `extra.metadata` 中的其他字段可能会用于估算 token 计数。以下字段按优先级顺序使用:
metadata.ls_model_nameinputs.modelinputs.model_name
提供Token和成本信息
默认情况下,LangSmith 使用 tiktoken 来计算 token,根据提供的 ls_model_name 对模型的 tokenizer 进行最佳猜测。它还通过使用模型定价表自动计算成本。要了解 LangSmith 如何计算基于 token 的成本,请参阅本指南。
然而,许多模型在响应中已经包含了精确的 token 计数。如果您有这些信息,您可以通过以下两种方式之一覆盖 LangSmith 中的默认 token 计算:
- 在您的追踪函数中提取使用情况,并在运行的元数据上设置一个 `usage_metadata` 字段。
- 在您的追踪函数输出中返回一个 `usage_metadata` 字段。
在这两种情况下,您发送的使用元数据应包含以下 LangSmith 识别字段的子集:
您不能设置除以下列出的字段之外的任何字段。您不需要包含所有字段。
class UsageMetadata(TypedDict, total=False):
input_tokens: int
"""The number of tokens used for the prompt."""
output_tokens: int
"""The number of tokens generated as output."""
total_tokens: int
"""The total number of tokens used."""
input_token_details: dict[str, float]
"""The details of the input tokens."""
output_token_details: dict[str, float]
"""The details of the output tokens."""
input_cost: float
"""The cost of the input tokens."""
output_cost: float
"""The cost of the output tokens."""
total_cost: float
"""The total cost of the tokens."""
input_cost_details: dict[str, float]
"""The cost details of the input tokens."""
output_cost_details: dict[str, float]
"""The cost details of the output tokens."""
请注意,使用数据还可以包含成本信息,以防您不想依赖 LangSmith 的基于 token 的成本公式。这对于定价与 token 类型不成线性关系的模型很有用。
设置运行元数据
您可以在追踪函数中修改当前运行的元数据以包含使用信息。这种方法的优点是您不需要更改追踪函数的运行时输出。这是一个示例:
需要 `langsmith>=0.3.43` (Python) 和 `langsmith>=0.3.30` (JS/TS)。
- Python
- TypeScript
from langsmith import traceable, get_current_run_tree
inputs = [
{"role": "system", "content": "You are a helpful assistant."},
{"role": "user", "content": "I'd like to book a table for two."},
]
@traceable(
run_type="llm",
metadata={"ls_provider": "my_provider", "ls_model_name": "my_model"}
)
def chat_model(messages: list):
llm_output = {
"choices": [
{
"message": {
"role": "assistant",
"content": "Sure, what time would you like to book the table for?"
}
}
],
"usage_metadata": {
"input_tokens": 27,
"output_tokens": 13,
"total_tokens": 40,
"input_token_details": {"cache_read": 10},
# If you wanted to specify costs:
# "input_cost": 1.1e-6,
# "input_cost_details": {"cache_read": 2.3e-7},
# "output_cost": 5.0e-6,
},
}
run = get_current_run_tree()
run.set(usage_metadata=llm_output["usage_metadata"])
return llm_output["choices"][0]["message"]
chat_model(inputs)
import { traceable, getCurrentRunTree } from "langsmith/traceable";
const messages = [
{ role: "system", content: "You are a helpful assistant." },
{ role: "user", content: "I'd like to book a table for two." },
];
const chatModel = traceable(
async ({
messages,
}: {
messages: { role: string; content: string }[];
model: string;
}) => {
const llmOutput = {
choices: [
{
message: {
role: "assistant",
content: "Sure, what time would you like to book the table for?",
},
},
],
usage_metadata: {
input_tokens: 27,
output_tokens: 13,
total_tokens: 40,
},
};
const runTree = getCurrentRunTree();
runTree.metadata.usage_metadata = llmOutput.usage_metadata;
return llmOutput.choices[0].message;
},
{ run_type: "llm", name: "chat_model", metadata: { ls_provider: "my_provider", ls_model_name: "my_model" } }
);
await chatModel({ messages });
设置运行输出
您可以在函数的响应中添加一个 `usage_metadata` 键,以手动设置 token 计数和成本。
- Python
- TypeScript
from langsmith import traceable
inputs = [
{"role": "system", "content": "You are a helpful assistant."},
{"role": "user", "content": "I'd like to book a table for two."},
]
output = {
"choices": [
{
"message": {
"role": "assistant",
"content": "Sure, what time would you like to book the table for?"
}
}
],
"usage_metadata": {
"input_tokens": 27,
"output_tokens": 13,
"total_tokens": 40,
"input_token_details": {"cache_read": 10},
# If you wanted to specify costs:
# "input_cost": 1.1e-6,
# "input_cost_details": {"cache_read": 2.3e-7},
# "output_cost": 5.0e-6,
},
}
@traceable(
run_type="llm",
metadata={"ls_provider": "my_provider", "ls_model_name": "my_model"}
)
def chat_model(messages: list):
return output
chat_model(inputs)
import { traceable } from "langsmith/traceable";
const messages = [
{ role: "system", content: "You are a helpful assistant." },
{ role: "user", content: "I'd like to book a table for two." },
];
const output = {
choices: [
{
message: {
role: "assistant",
content: "Sure, what time would you like to book the table for?",
},
},
],
usage_metadata: {
input_tokens: 27,
output_tokens: 13,
total_tokens: 40,
},
};
const chatModel = traceable(
async ({
messages,
}: {
messages: { role: string; content: string }[];
model: string;
}) => {
return output;
},
{ run_type: "llm", name: "chat_model", metadata: { ls_provider: "my_provider", ls_model_name: "my_model" } }
);
await chatModel({ messages });
指令风格模型
对于指令风格模型(字符串输入,字符串输出),您的输入必须包含一个键 `prompt`,其值为字符串。也允许其他输入。输出必须返回一个对象,该对象在序列化后包含键 `choices`,其值为字典/对象列表。每个字典/对象必须包含键 `text`,其值为字符串。`metadata` 和 `usage_metadata` 的规则与聊天风格模型相同。
- Python
- TypeScript
@traceable(
run_type="llm",
metadata={"ls_provider": "my_provider", "ls_model_name": "my_model"}
)
def hello_llm(prompt: str):
return {
"choices": [
{"text": "Hello, " + prompt}
],
"usage_metadata": {
"input_tokens": 4,
"output_tokens": 5,
"total_tokens": 9,
},
}
hello_llm("polly the parrot\n")
import { traceable } from "langsmith/traceable";
const helloLLM = traceable(
({ prompt }: { prompt: string }) => {
return {
choices: [
{ text: "Hello, " + prompt }
],
usage_metadata: {
input_tokens: 4,
output_tokens: 5,
total_tokens: 9,
},
};
},
{ run_type: "llm", name: "hello_llm", metadata: { ls_provider: "my_provider", ls_model_name: "my_model" } }
);
await helloLLM({ prompt: "polly the parrot\n" });
以上代码将记录以下追踪