评估快速入门
评估是一种量化衡量 LLM 应用程序性能的方法,这很重要,因为 LLM 的行为并非总能预测——提示、模型或输入的微小变化都可能显著影响结果。评估提供了一种结构化的方式来识别故障,比较应用程序不同版本之间的变化,并构建更可靠的 AI 应用程序。
评估由三个组件构成
- 包含测试输入和可选预期输出的数据集。
- 定义您正在评估内容的目标函数。例如,这可能是一个包含您正在测试的新提示的 LLM 调用、您的应用程序的一部分或您的端到端应用程序。
- 对目标函数输出进行评分的评估器。
本快速入门将指导您运行一个简单的评估,以使用 LangSmith SDK 或 UI 测试 LLM 响应的正确性。
- SDK
- UI
本快速入门使用来自开源 openevals 包的预置 LLM-as-a-judge 评估器。OpenEvals 包含一组常用的评估器,如果您是评估新手,这是一个很好的起点。如果您希望在评估应用程序方面拥有更大的灵活性,您还可以使用您自己的代码定义完全自定义的评估器。
1. 安装依赖项
- Python
- TypeScript
pip install -U langsmith openevals openai
npm install langsmith openevals openai
如果您使用 yarn 作为包管理器,您还需要手动安装 @langchain/core 作为 openevals 的对等依赖项。这通常不是 LangSmith 评估所必需的——您可以使用任意自定义代码定义评估器。
2. 创建 LangSmith API 密钥
要创建 API 密钥,请前往设置页面。然后点击创建 API 密钥。
3. 设置您的环境
由于本快速入门使用 OpenAI 模型,您需要设置 OPENAI_API_KEY 环境变量以及所需的 LangSmith 变量
- Shell
export LANGSMITH_TRACING=true
export LANGSMITH_API_KEY="<your-langchain-api-key>"
# This example uses OpenAI, but you can use other LLM providers if desired
export OPENAI_API_KEY="<your-openai-api-key>"
4. 创建数据集
接下来,定义您将用于评估应用程序的示例输入和参考输出对
- Python
- TypeScript
from langsmith import Client
client = Client()
# Programmatically create a dataset in LangSmith
# For other dataset creation methods, see:
# https://langsmith.langchain.ac.cn/evaluation/how_to_guides/manage_datasets_programmatically
# https://langsmith.langchain.ac.cn/evaluation/how_to_guides/manage_datasets_in_application
dataset = client.create_dataset(
dataset_name="Sample dataset", description="A sample dataset in LangSmith."
)
# Create examples
examples = [
{
"inputs": {"question": "Which country is Mount Kilimanjaro located in?"},
"outputs": {"answer": "Mount Kilimanjaro is located in Tanzania."},
},
{
"inputs": {"question": "What is Earth's lowest point?"},
"outputs": {"answer": "Earth's lowest point is The Dead Sea."},
},
]
# Add examples to the dataset
client.create_examples(dataset_id=dataset.id, examples=examples)
import { Client } from "langsmith";
const client = new Client();
// Programmatically create a dataset in LangSmith
// For other dataset creation methods, see:
// https://langsmith.langchain.ac.cn/evaluation/how_to_guides/manage_datasets_programmatically
// https://langsmith.langchain.ac.cn/evaluation/how_to_guides/manage_datasets_in_application
const dataset = await client.createDataset("Sample dataset", {
description: "A sample dataset in LangSmith.",
});
// Create inputs and reference outputs
const examples = [
{
inputs: { question: "Which country is Mount Kilimanjaro located in?" },
outputs: { answer: "Mount Kilimanjaro is located in Tanzania." },
dataset_id: dataset.id,
},
{
inputs: { question: "What is Earth's lowest point?" },
outputs: { answer: "Earth's lowest point is The Dead Sea." },
dataset_id: dataset.id,
},
];
// Add examples to the dataset
await client.createExamples(examples);
5. 定义您正在评估的内容
现在,定义包含您正在评估内容的目标函数。例如,这可能是一个包含您正在测试的新提示的 LLM 调用、您的应用程序的一部分或您的端到端应用程序。
- Python
- TypeScript
from langsmith import wrappers
from openai import OpenAI
# Wrap the OpenAI client for LangSmith tracing
openai_client = wrappers.wrap_openai(OpenAI())
# Define the application logic you want to evaluate inside a target function
# The SDK will automatically send the inputs from the dataset to your target function
def target(inputs: dict) -> dict:
response = openai_client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-4o-mini",
messages=[
{"role": "system", "content": "Answer the following question accurately"},
{"role": "user", "content": inputs["question"]},
],
)
return { "answer": response.choices[0].message.content.strip() }
import { wrapOpenAI } from "langsmith/wrappers";
import OpenAI from "openai";
const openai = wrapOpenAI(new OpenAI());
// Define the application logic you want to evaluate inside a target function
// The SDK will automatically send the inputs from the dataset to your target function
async function target(inputs: { question: string }): Promise<{ answer: string }> {
const response = await openai.chat.completions.create({
model: "gpt-4o-mini",
messages: [
{ role: "system", content: "Answer the following question accurately" },
{ role: "user", content: inputs.question },
],
});
return { answer: response.choices[0].message.content?.trim() || "" };
}
6. 定义评估器
从 openevals 导入预置提示并创建评估器。outputs 是目标函数的结果。reference_outputs / referenceOutputs 来自您在上述第 4 步中定义的示例对。
CORRECTNESS_PROMPT 只是一个 f-string,包含 `"inputs"`、`"outputs"` 和 `"reference_outputs"` 变量。有关自定义 OpenEvals 提示的更多信息,请参阅此处。
- Python
- TypeScript
from openevals.llm import create_llm_as_judge
from openevals.prompts import CORRECTNESS_PROMPT
def correctness_evaluator(inputs: dict, outputs: dict, reference_outputs: dict):
evaluator = create_llm_as_judge(
prompt=CORRECTNESS_PROMPT,
model="openai:o3-mini",
feedback_key="correctness",
)
eval_result = evaluator(
inputs=inputs,
outputs=outputs,
reference_outputs=reference_outputs
)
return eval_result
import { createLLMAsJudge, CORRECTNESS_PROMPT } from "openevals";
const correctnessEvaluator = async (params: {
inputs: Record<string, unknown>;
outputs: Record<string, unknown>;
referenceOutputs?: Record<string, unknown>;
}) => {
const evaluator = createLLMAsJudge({
prompt: CORRECTNESS_PROMPT,
model: "openai:o3-mini",
feedbackKey: "correctness",
});
const evaluatorResult = await evaluator({
inputs: params.inputs,
outputs: params.outputs,
referenceOutputs: params.referenceOutputs,
});
return evaluatorResult;
};
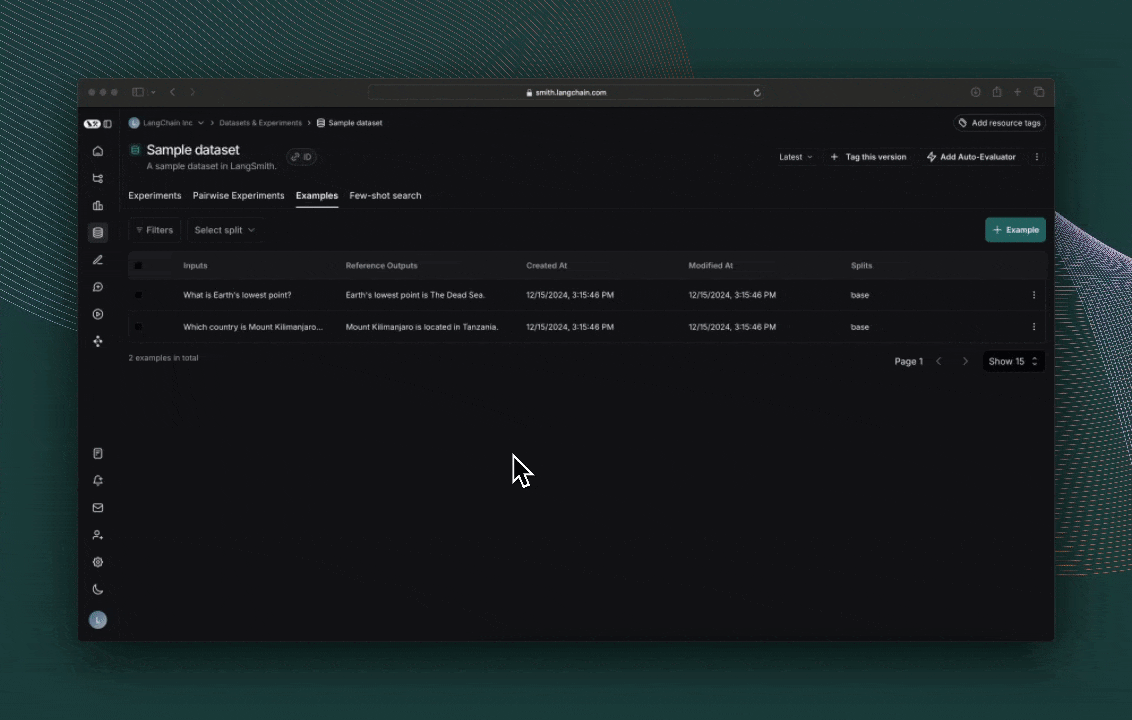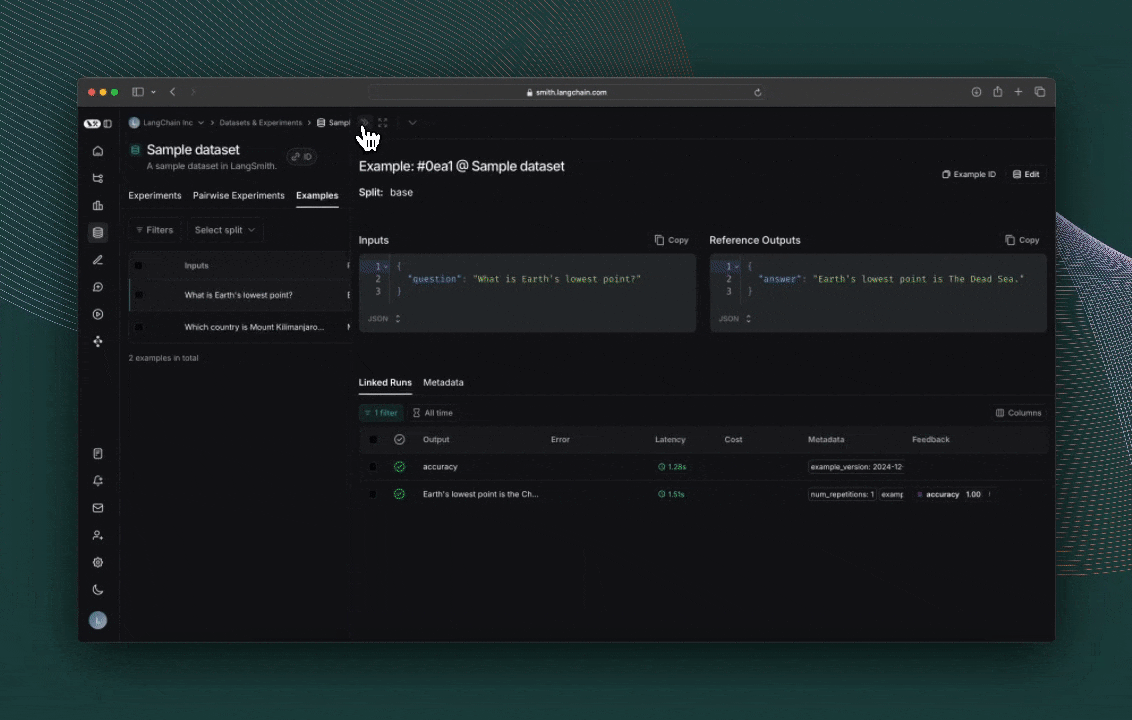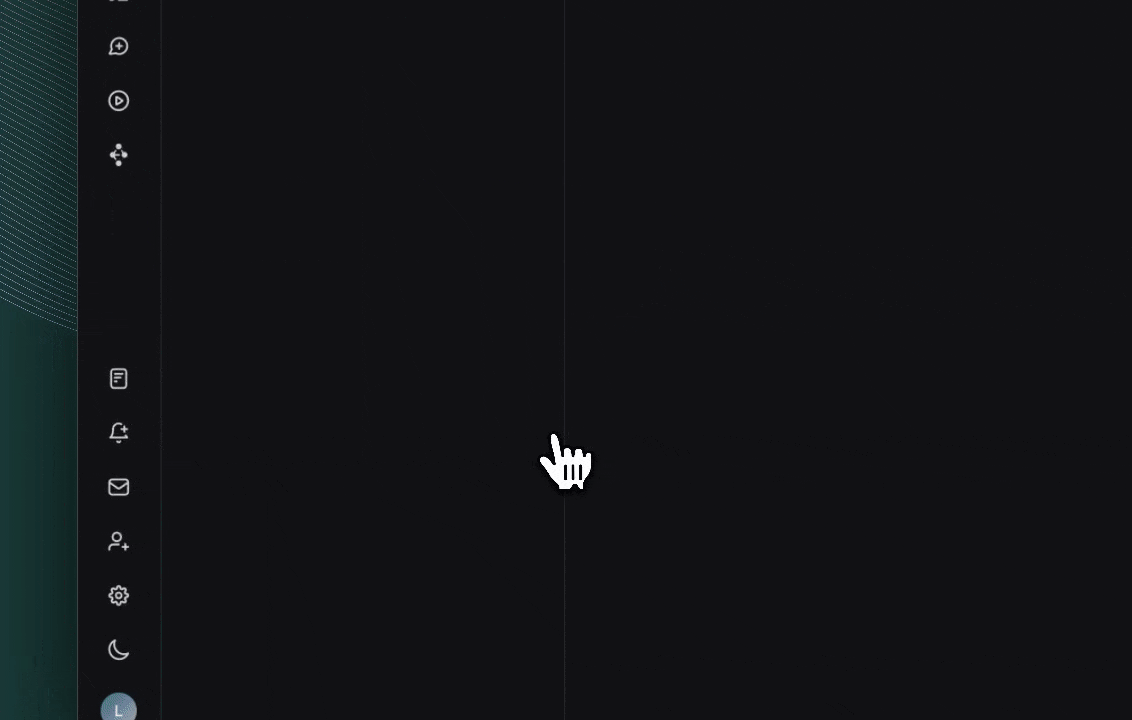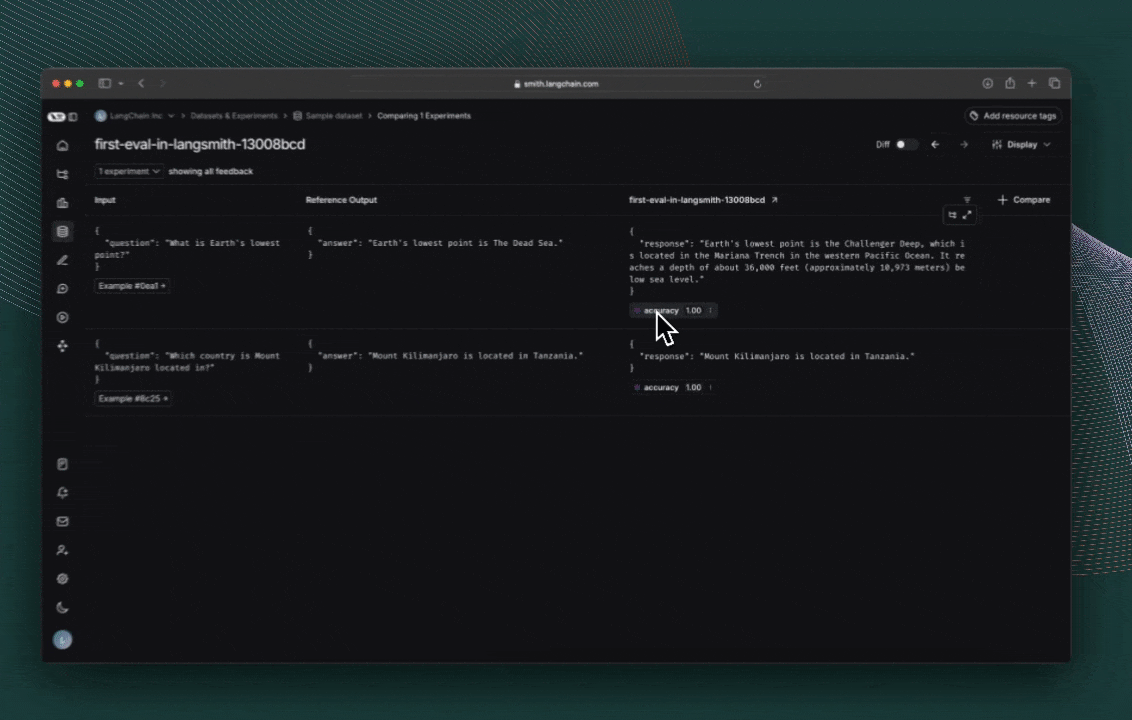
7. 运行并查看结果
最后,运行实验!
- Python
- TypeScript
# After running the evaluation, a link will be provided to view the results in langsmith
experiment_results = client.evaluate(
target,
data="Sample dataset",
evaluators=[
correctness_evaluator,
# can add multiple evaluators here
],
experiment_prefix="first-eval-in-langsmith",
max_concurrency=2,
)
import { evaluate } from "langsmith/evaluation";
// After running the evaluation, a link will be provided to view the results in langsmith
await evaluate(
target,
{
data: "Sample dataset",
evaluators: [
correctnessEvaluator,
// can add multiple evaluators here
],
experimentPrefix: "first-eval-in-langsmith",
maxConcurrency: 2,
}
);
点击评估运行打印出的链接,访问 LangSmith 实验 UI,并探索实验结果。
下一步
要了解有关在 LangSmith 中运行实验的更多信息,请阅读评估概念指南。
- 查看 OpenEvals README,了解所有可用的预置评估器以及如何自定义它们。
- 了解如何定义包含任意代码的自定义评估器。
- 查看操作指南以获取“我该如何……?”格式问题的答案。
- 有关端到端演练,请参阅教程。
- 有关每个类和函数的详细描述,请参阅API 参考。
或者,如果您喜欢视频教程,请查看 LangSmith 简介课程中的数据集、评估器和实验视频。
1. 导航到试验场
LangSmith 的提示词试验场使您能够对不同的提示、新模型或测试不同的模型配置运行评估。前往 LangSmith UI 中的试验场。
2. 创建提示词
修改系统提示词为
Answer the following question accurately:
3. 创建数据集
点击设置评估,然后使用下拉菜单中的+ 新建按钮创建新数据集。
将以下示例添加到数据集
| 输入 | 参考输出 |
|---|---|
| 问题:乞力马扎罗山位于哪个国家? | 输出:乞力马扎罗山位于坦桑尼亚。 |
| 问题:地球的最低点是哪里? | 输出:地球的最低点是死海。 |
点击保存以保存您新创建的数据集。
4. 添加评估器
点击+评估器。从预置评估器选项中选择正确性。点击保存。
5. 运行您的评估
点击右上角的开始以运行评估。运行此评估将创建一个实验,您可以通过点击实验名称来完整查看。

下一步
要了解有关在 LangSmith 中运行实验的更多信息,请阅读评估概念指南。
查看操作指南以获取“我该如何……?”格式问题的答案。
- 了解如何在UI 中创建和管理数据集
- 了解如何从提示词试验场运行评估
如果您喜欢视频教程,请查看 LangSmith 简介课程中的试验场视频。